The common causes of back pain in athletes include:
These measures help to relieve your back pain and in the vast majority of cases people will improve in a period of 4-12 weeks. In certain circumstances, some people do not improve and a referral to a Consultant is required for further intervention such as spinal injections, and very occasionally, surgery. If this is the case, our physiotherapist will be able to advise you and facilitate onward referral.
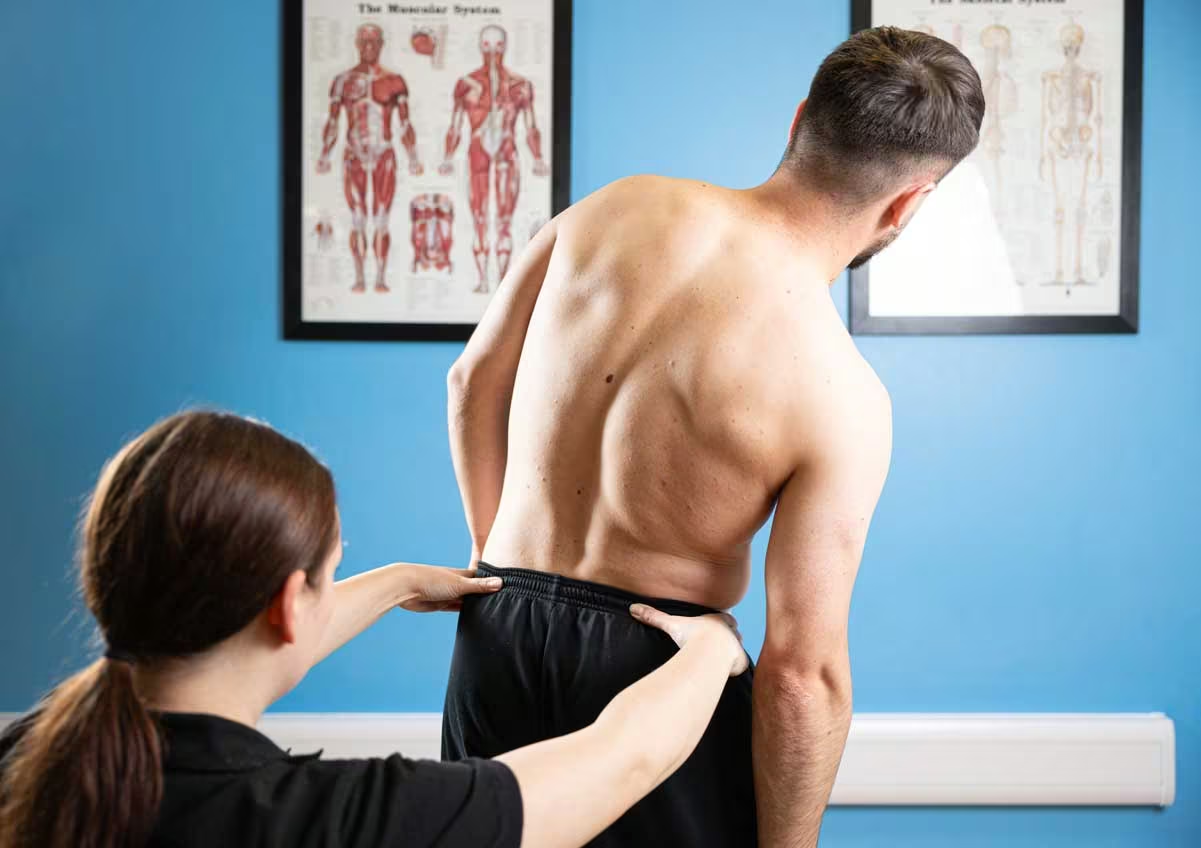
Low back pain is often a common symptom of many disease conditions and the back pain may range from simple or dull pain to sudden and sharp pain. If the pain persists for a few days, it is acute pain whereas if it continues for more than 3 months, it is considered as chronic pain. In most cases, low back pain may resolve without any treatment, however, if it persists for more than 3 days, medical intervention is necessary.
Low back pain may be a common symptom in various conditions such as appendicitis, aneurysms, kidney diseases, kidney and bladder infections, ovarian disorders, pregnancy, nerve root syndromes such as sciatica, herniated discs, spinal stenosis, musculoskeletal problems, osteomyelitis, spondylitis, tumors, spine injuries, fractures, and many more.
Low back pain can be alleviated with rest and RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, and elevation) treatment, pain relievers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, and physical therapy. However, certain conditions causing severe pain may require surgical treatment. Treating the underlying conditions offers relief from back pain.
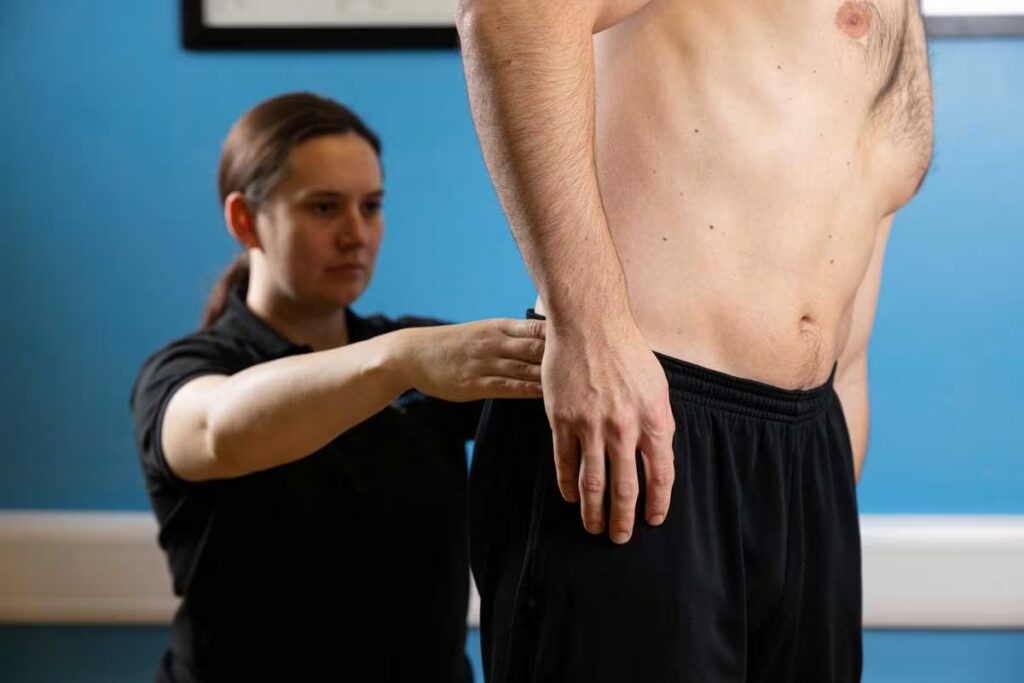
One of the common causes of low back pain is a low back strain. Low back strain or lumbar strain occurs when the muscle or the tendon in the lower back gets stretched or torn. It is caused by lifting heavy objects or overload, sitting or standing for a longer time, direct blow over the area, or sports such as basketball, baseball, or golf that involve sudden twisting of the lower back, can also lead to strain.
The risk factors such as excess low back curvature, weak abdominal muscles, and forwardly tilted pelvis can increase the risk of this injury. The common symptoms include low back pain that radiates down to the buttocks; inflammation of the soft tissues that surround the muscles; stiffness in the lower back; restricted movements; inability to maintain correct posture; muscle spasms; and pain which continues for a longer period.
Conservative treatment methods include: