Damage to any of the structures that make up the elbow joint can cause elbow pain.
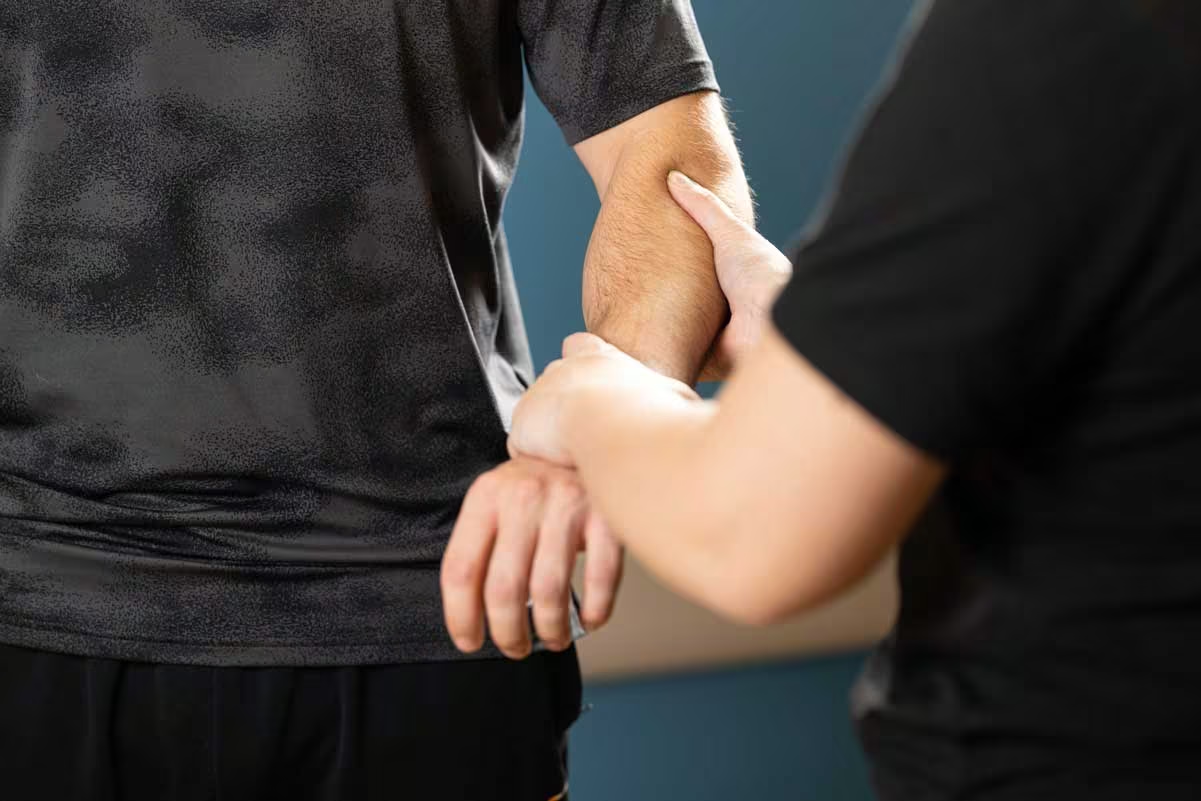
An elbow dislocation occurs when the bones that make up the joint are forced out of alignment as when you fall onto an outstretched hand. They can also occur from any traumatic injury such as motor vehicle accidents. When the elbow is dislocated you may experience severe pain, swelling, and lack of ability to bend your arm. Sometimes, you cannot feel your hand or may have no pulse in your wrist because arteries and nerves that run along your elbow may be injured.
Tennis elbow is the inflammation of muscles on the outside of the elbow whereas tendinitis on the inner side of the elbow is golfer’s elbow. Overuse of the arms or a traumatic blow to the hand may cause tennis elbow or golfer’s elbow. These injuries may cause severe pain and tenderness of the affected muscles that radiate down into the forearm, particularly with the use of the hand and wrist.
Adequate rest and immobility of the affected part help the muscles to recover and modification of the activities helps in better healing. A tennis elbow strap may relieve the pressure from the muscle attachment. Pain medications may be recommended to relieve pain and inflammation. Heat therapy, followed by stretching and strengthening exercises and then ice massage may be beneficial.
For more information on Tennis/Golfers elbow click here.
Tendonitis is inflammation of any of the tendons in the wrist. It is usually treated with adequate rest, splinting, ice application and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines to reduce the inflammation.
Any problem causing pain, swelling, discolouration, numbness, or a tingling sensation, or abnormal position of the elbow that persists for more than two or three days should be evaluated by your doctor to establish the cause and obtain the best treatment as early as possible.
The elbow joint is made up of three bones: the humerus (upper arm bone), and the radius and ulna (the forearm bones). It consists of a hinge joint that permits flexion and extension of the arm, and a ball-and-socket joint that enables rotation of the wrist. There are three bony junctions in the elbow: the proximal radioulnar joint between the radius and ulna, the ulnohumeral joint between the ulna and humerus, and the radiohumeral joint between the humerus and the radius. The bones are held in position by a number of ligaments.
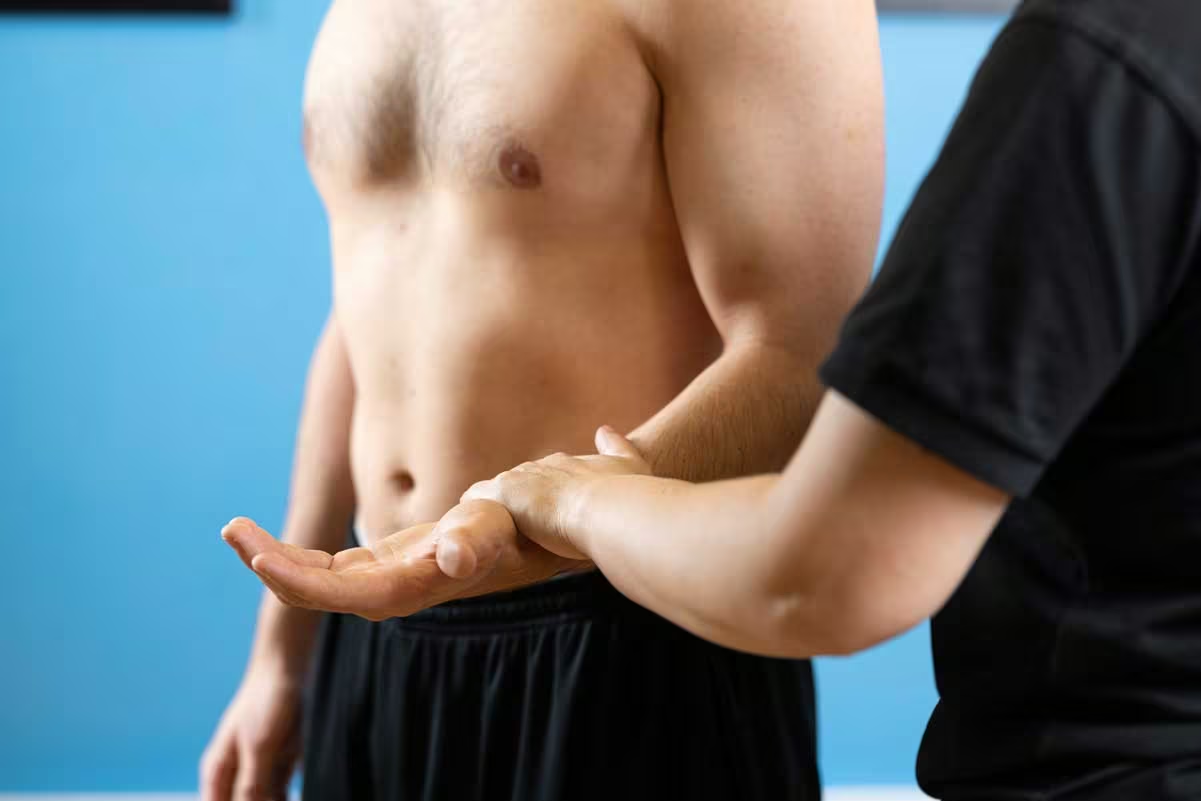
The various signs and symptoms of elbow instability include:
Your doctor will diagnose elbow instability based on your medical history and a physical examination. Once the preliminary diagnosis is complete, your doctor may use imaging techniques such as X-ray, MRI, or MRI arthrography to obtain a detailed view of the elbow and look for other injuries.
Different treatment methods are used based on the severity of the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Most cases of elbow instability can be managed by nonsurgical treatment including rest, activity modification, and physical therapy. Your doctor may perform an external reduction if the elbow is dislocated. A sling or brace may be used to keep the elbow immobile for a specific duration to facilitate healing. Simple motion exercises may be recommended to improve strength and movement.
Surgical Treatment
In some cases, surgical treatment may be necessary to restore elbow alignment and stability. This may involve repair or reconstruction of damaged ligaments and realignment of the bones in cases of fracture or dislocation. Once this is complete, an external fixator device may be used to support the joint and facilitate healing. In some cases, surgery may be required to repair damaged blood vessels and nerves. A defined recovery period and physical therapy are recommended following surgery.